Hohenstieglen pilot project
The Hohenstieglen retaining structure along the N01 national road in the municipalities of Opfikon and Zurich is being repaired and fitted with new solar panels (see Fig. 1). The existing Hohenstieglen retaining structure is an "evergreen wall" that is being rebuilt (see Fig. 2).

Figure 1: Overview of the project perimeter: Construction of the photovoltaic system in the area marked in yellow

Figure 2: Initial situation of the Hohenstieglen retaining structure
For the project, a variant with an inclination of 76° and a variant with an inclination of 36° of the solar panels were basically under discussion. For the 36° variant, the effect of a sound-absorbing rear wall was also tested.
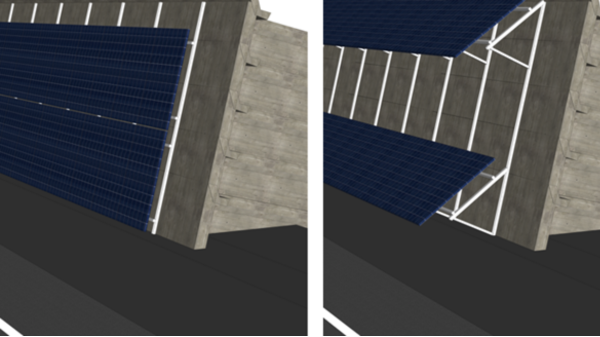
Abbildung 3: Geprüfte Varianten: links Variante 76°, rechts Variante 36° (Quelle: TNC Engineering AG)
Acoustic assessment
In collaboration with the Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Testing and Research (Empa), simulations were used to analyse the changes in sound reflections compared to the initial state and the effects on overall noise. The reflection index of the existing retaining structure was recorded in the field using a measurement system developed by Empa.
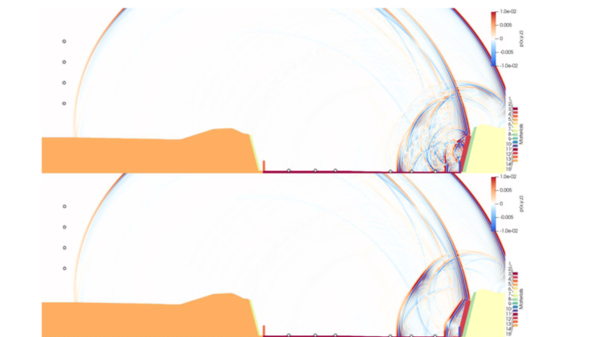
Figure 4: Wave-theoretical sound field simulations in the terrain cross-section for the investigation of sound reflections (sound pressure coded red-blue): Above 36° variant, below 76° variant (source: Empa)

Figure 5: Empa measurement system and reflection index measurement of the Evergreen-Wall Hohenstieglen (Source: Empa)
The analysis of the results shows that the 36° variant, which was also fitted with a sound-absorbing rear wall, causes the fewest sound reflections. However, in the case of the 36° variant with a sound-absorbing rear wall and the 76° variant, the increase in noise due to reflections is negligible in the present situation, as the reflected sound plays a subordinate role compared to the direct sound of the motorway. Based on the findings and in view of the costs, maintenance, technical feasibility, etc. of the planned PV system, it was decided to implement the 76° variant.
In order to test the actual acoustic effect of the solar panels, additional control measurements were carried out before (already carried out; see Fig. 6) and after the construction of the PV system, both inside and outside the acoustic influence area of the PV system.

Figure 6: Control measurement in the area of influence of the solar panels (measuring point marked in red)
Conclusion and outlook
The investigations carried out show that, in addition to the position and orientation of the solar panels, the local conditions, such as the surrounding terrain, the location of the neighbouring residential properties, the distance between the roadway and the PV system, etc., also have a significant influence on the noise situation for residents. The acoustic impact of PV systems on transport infrastructure must be assessed on a case-by-case basis and the position and orientation of the solar panels adapted to local conditions. Through forward-looking planning, as demonstrated in this pilot project in collaboration with FEDRO, Empa and TNC Engineering AG, the potential of motorways for PV systems can be exploited without any perceptible noise-increasing effect on local residents.
Links to further websites:
/www.gundp.ch/file/2738/akustische-beurteilung-von-pv-anlagen-autobahn.png)
/www.gundp.ch/file/1950/Strassenlaerm_Tempo30_Laermarmer_Belag.png)
/www.gundp.ch/file/2109/Titelbild_3D_Texturmessung.png)
/www.gundp.ch/file/2849/Data_Science_E.png)